Cracked Teeth
Cracked teeth are a very common dental problem that millions of people deal with every single year. There are several different types of cracked teeth that can be fixed with endodontic surgery, while other types are more severe and would require extraction of the tooth. The main causes of cracked teeth are as follows:
Chewing on hard objects such as ice, candy, pens, and other hard foods.
Clinching and/or grinding your teeth.
How will you know if your tooth is cracked?
Typically a cracked tooth will cause pain when chewing or exposing it to extreme temperature changes. The pain can commonly come and go making it difficult for your dentist or endodontist to locate the problem tooth.
What causes a cracked tooth to hurt?
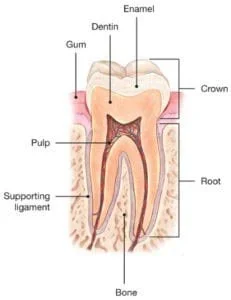
When a tooth becomes cracked, the different pieces can shift while chewing which can lead to irritation of the pulp(which contains the nerves and blood vessels).
After enough times of continued irritation, the pulp loses its ability to heal itself.
Extensive cracks can lead to infection of the pulp tissue, which can spread to the bone and gum surrounding the tooth.
Chipped tooth vs cracked tooth?
Chipped
A chipped tooth is a tooth with a piece broken off.
Most chipped teeth can be repaired either by reattaching the broken piece of tooth enamel or by bonding a tooth-colored filling or crown in place.
Chipped teeth are the most common type of dental injury.
Cracked
A cracked tooth almost always has a vertical fracture that can range anywhere from the surface all the way down into the gums.
Cracked teeth almost always require surgery to repair and sometimes even require extraction of the tooth.
While typically not a severe issue in general, a cracked tooth is much more problematic than a chipped tooth.
Types of cracked teeth.
-
Tiny cracks that affect only the outer enamel and are extremely common in adult teeth. Craze lines are very shallow, cause no pain, and are of no concern beyond appearances.
-
When a piece of a tooth’s chewing surface breaks off, often around a filling. Typically, a fractured cusp doesn’t cause much pain and rarely damages the pulp.
-
A cracked tooth means a crack extends from the chewing surface of your tooth vertically toward the root. The tooth is not yet separated into pieces, though the crack may gradually spread.
Early diagnosis is important in order to save the tooth. If the crack has extended into the pulp, the tooth can be treated with a root canal procedure and a crown to protect the crack from spreading.
However, if the crack extends below the gum line, it is no longer treatable, and the tooth cannot be saved and will need to be extracted. That’s why early treatment is so important. A cracked tooth that is not treated will progressively worsen, eventually resulting in the loss of the tooth.
Early diagnosis and treatment are essential in saving these teeth.
-
Often the result of the long term progression of a cracked tooth. The split tooth is identified by a crack with distinct segments that can be separated.
A split tooth cannot be saved intact. The position and extent of the crack, however, will determine whether any portion of the tooth can be saved.
In some cases, a root canal or endodontic surgery may be performed to save a portion of the tooth.
-
Cracks that begin in the root of the tooth and extend toward the chewing surface. They often show minimal signs and symptoms and may therefore go unnoticed for some time.
Vertical root fractures are often discovered when the surrounding bone and gum become infected.
Treatment may involve extraction of the tooth. However, endodontic surgery is sometimes appropriate if a tooth can be saved by removal of the fractured portion.
Fractured Cusp
Cracked Teeth
Split Tooth
Vertical Root Fracture
Does your cracked tooth completely heal after treatment?
Unlike a broken bone, a cracked tooth does not heal.
Even after treatment, some cracks will continue to spread and worsen over time.
Placing a crown on the cracked tooth provides maximum protection, but does not guarantee success in all cases.
Treatment will relieve pain and reduce the risk of further separation. Once treated most teeth will function normally for many years.